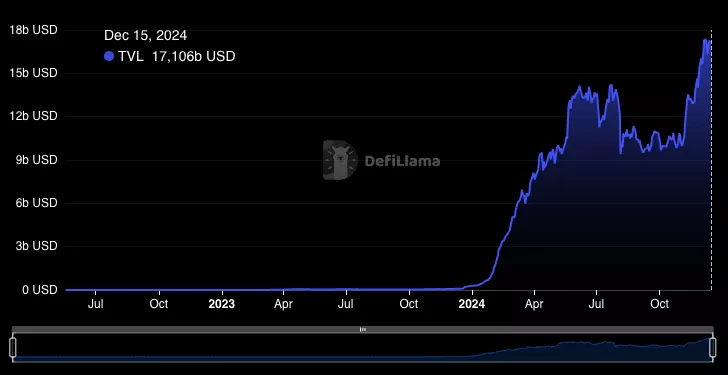
The Solana blockchain infrastructure is seeing a significant contraction in its participant base. Recent data from The Block Research reveals that the number of daily active validators has dropped to 800—the lowest point recorded since 2021.
The Downward Trend
Current figures present a sharp contrast to the network’s period of rapid expansion. The table below illustrates the decline in key performance metrics:
| Metric | 2023 Peak | Current (Early 2026) | Change |
| Active Validators | > 2,500 | 800 | -65% |
| Voting Transactions | 300,000 / day | 170,000 / day | -43% |
Why Are Validators Leaving?
The primary driver behind this mass exodus is economic sustainability. Operating a node on the Solana network requires high-end hardware and constant operational costs, which have become increasingly difficult for smaller players to manage.
Key Pressures Include:
- Reduced Support from Solana Foundation: The Delegation Program, which previously subsidized voting costs and provided “stake-matching” support, is tapering off.
- High Barrier to Entry: Without a significant amount of delegated SOL (stake), the block rewards often fail to cover the high overhead of server infrastructure and data egress.
- Asset Lock-ups: Validators must lock up substantial assets to remain synchronized with the network. In the current economic climate, the “break-even point” has become unreachable for many independent operators.
Note: Despite the decline in validator nodes, end-user activity remains resilient. Non-voting transactions have held steady at approximately 150 million per day, suggesting that demand for the network’s services remains high.
Looking Ahead: The Quantum Threat
While the network navigates these structural shifts, the Solana Foundation is pivoting its focus toward long-term security. In December 2025, the Foundation announced a strategic partnership with Project Eleven.
The goal of this collaboration is to prepare the network for the era of quantum computing. By integrating post-quantum cryptographic algorithms, Solana aims to future-proof its architecture against next-generation threats, even as it works to stabilize its current validator ecosystem.