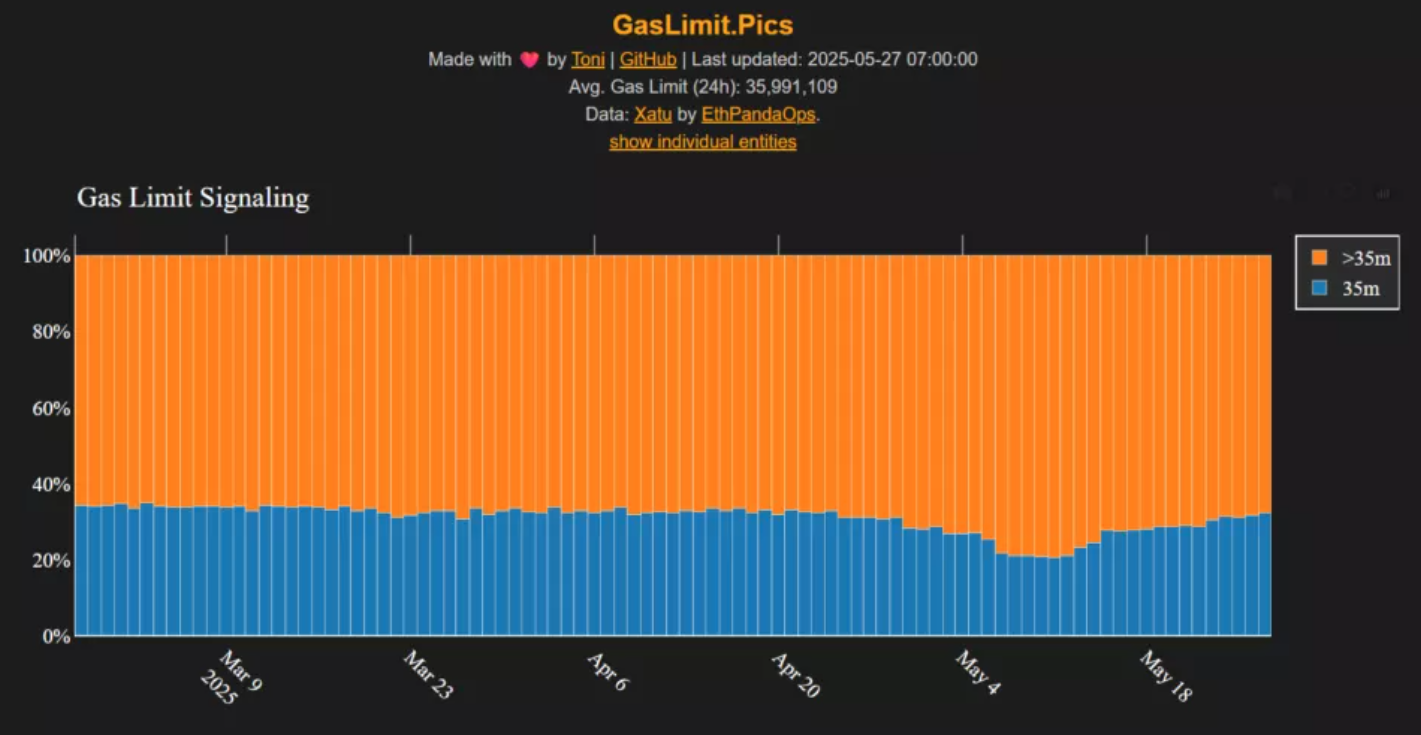
Over 150,000 Ethereum validators—approximately 15% of the total network participants—have expressed support for raising the gas limit from the current 36 million to 60 million. This move aims to increase the network’s throughput: by raising the limit, each block can process more transactions and data, potentially reducing fees and speeding up transaction times during periods of peak demand.
📈 What This Means for the Network:
- Higher Throughput. More transactions per block means less competition for inclusion, which can help lower average gas fees.
- A Step Toward Scalability. Raising the gas limit is seen as a temporary measure to boost performance until larger upgrades like Danksharding and full implementation of Proto-Danksharding (EIP-4844) are rolled out.
⚙️ How the Change Will Be Implemented:
- Updating the Ethereum gas limit does not require a hard fork or a new protocol release. It’s achieved through a decentralized process: once over 50% of validators manually adjust their nodes to the new limit, the change will be applied automatically across the network.
- This approach minimizes the risk of a network split and makes the transition simpler for participants.
🕒 Historical Context:
- The gas limit has been increased several times in the past:
- In 2021, it was raised from 15 million to 30 million.
- In February 2024, it was increased from 30 million to 36 million.
Each adjustment has sparked active debates in the community about potential impacts on the network.
⚠️ Risks and Developer Concerns:
- Some developers and community members warn that a higher gas limit will lead to increased hardware requirements for node operators.
- Why It Matters: Larger blocks mean more data to process and store, which could create barriers for smaller validators and make it harder for them to participate in securing the network.
- Additionally, larger blocks could raise the risk of centralization: if running a full node becomes too resource-intensive, only well-funded entities may be able to maintain validator status.
🌐 Ethereum’s Long-Term Vision:
- On May 19, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin proposed reducing the node state size to ease the burden on network participants and make running validators more accessible. This idea is part of a broader strategy to optimize Ethereum’s architecture, including the upcoming Proto-Danksharding upgrade (EIP-4844), which aims to reduce the load on the base layer.
💬 Community Perspective:
- The gas limit increase is seen as a temporary solution to improve scalability, but in the long run, the focus remains on protocol-level optimizations such as Danksharding, Rollups, and data storage enhancements.
- Some community members are concerned that continuously raising the gas limit without addressing core architectural challenges could lead to excessive centralization and undermine Ethereum’s decentralized nature.